As a survey creator, it is natural for you to expect encouraging and reliable responses to your surveys. With an enhanced survey response rate, the chances of collecting accurate data increases.
But unfortunately, not all surveys are error free.
Many surveys face the problem of survey bias leading to inaccurate and unreliable feedback collection. Survey bias is a situation where your survey respondents end up giving feedback in a predetermined and unnatural way. This could be because of many factors like incorrect wording of questions, confused order of answer options, survey respondents’ personal beliefs, and so on.

Image Source: Essentia Analytics Ltd
Survey bias forces your target audience to be either too pleasing or extremely negative, give reluctant feedback, or put forth a dishonest opinion.
Survey bias can be reduced with careful research and planning. This blog gives you a thorough understanding of the types of survey bias and the ways to eliminate survey bias with ease.
What is Survey Bias?
The term bias means having a strong feeling of prejudice or affinity towards a particular group of people, objects, ideas, and so on. A bias can give rise to both positive as well as negative behaviours. For example, if you have an affinity towards meditation, it leads to a healthy and productive lifestyle. On the other hand, a prejudice against Jews in the World War II era resulted in the Holocaust (killing of Jews in the erstwhile Nazi Germany).
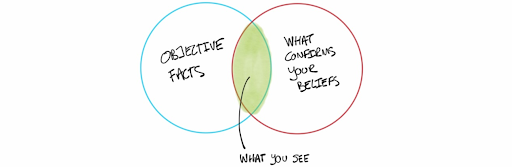
Image Source: Applied Frameworks
In case of a survey, bias refers to conditions or factors that can lead to inaccurate or dishonest responses from your target group. Either your audience may not have understood the question correctly or they are fearing non-anonymity, leading to twisted responses. When your audience is not free to speak out their mind, you will not be able to know the actual performance of your products and services.
In the next section, let’s understand the different types of survey biases along with the tips to eliminate survey bias.
Types of Survey Bias and Tips to Avoid Them
There are different types of survey biases resulting from various factors like survey wording, questions placement, and more.
1. Sampling Bias
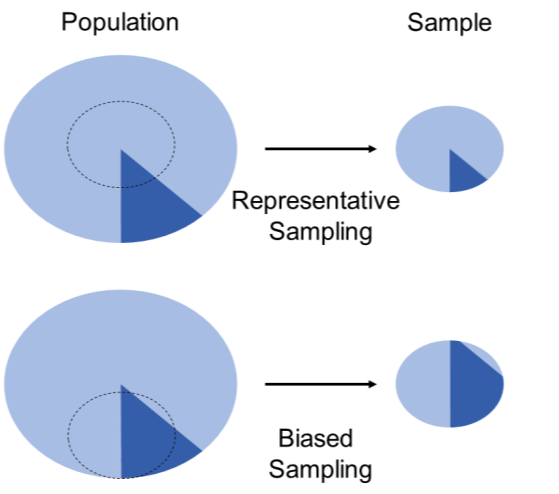
Image Source: ResearchGate
In this type of survey bias, the audience sample size for feedback collection is skewed and predetermined. The sampling is done solely with the intention of getting desirable feedback from the audience. In doing so, you are altogether eliminating the survey respondents who might give you negative feedback.
For example, when you collect feedback from only your loyal customers, you are excluding the constructive feedback of your former customers. Due to this sampling error, you lose out on the opportunity to enhance your products or services.
How to Avoid Sampling Bias?
Sampling bias can be tackled by understanding the outreach of your target audience.
(a) In some surveys it is necessary to eliminate a certain group of customers. Hence, understand the real goals and objectives of your survey to shortlist your survey respondents.
(b) Distribute your survey using maximum distribution channels like social media, email, website embedding, and more. Powerful survey tools like ProProfs Survey Maker comes with multiple survey sharing options which ensures that you do not miss out on any of your target audience.
(c) Create your customer journey map and ensure that you collect their feedback at every touchpoint.
2. Social Desirability Bias

Image Source: Carnegie Mellon University
Here, the survey takers respond in a favorable way to be in the good books of others. This tendency usually creeps in due to people’s desire to be associated with a particular group of people or a specific habit.
For example, a survey question “Do you exercise regularly?” can be met with a positive response from most of the survey respondents. In this case, most of the survey takers show a social desire to be seen as following healthy habits.
How to Avoid Social Desirability Bias?
(a) Make your survey anonymous to get more honest survey responses.
(b)Use positive or neutral wording of questions to get reliable answers.
For example, instead of asking “What do you dislike about the product?”, you can reframe the question in a positive manner as “What changes do you wish to see in the product?”
(c) Pose indirect questions to encourage your survey respondents to share their opinion.
For example, in an employee survey, instead of directly asking “How often do you come on time?”, you can indirectly ask, “How often do you see people coming on time to the office?”. While answering indirect questions, people do not feel judged and are more comfortable while responding to questions.
3. Acceptance and Dissent Bias
Acceptance and dissent bias is a type of response order bias. In an acceptance bias, your survey takers give an extremely positive response or ‘yes’ answer to every consecutive survey question. Comparatively, a dissent bias occurs when the survey takers give a negative response ‘no’ to every survey question.
This happens when you have a long survey with complex questions. People may not be willing to spend time reading through the questions to give thoughtful responses.
While it is good to see a positive response to your survey, the ‘yes’ answers are often given out of compulsion. Also, some people have a tendency to give only positive responses to not sound negative.
How to Avoid Response Bias in Your Survey?
(a) Avoid leading and loading types of questions which prompt your survey respondents to give a predetermined favorable response.
(b) Use a variety of question types in addition to ‘yes’ or ‘no’ type responses like open-ended questions, multiple choice questions, and more.
(c) Use cleverly phrased likert scale answer options by avoiding phrases like “Probably likely”, “Probably likely not”, and more.
4. Question Order Bias
Question order bias is a situation in which the survey respondents give a biased answer because of the type of the preceding question. The preceding question is framed in such a way that it makes your survey respondents to think and answer in a predetermined way.
Let’s consider some question order bias examples,
Q1: Did you like our product feature {X}?
Q2: Are you comfortable with our product user interface?
Q3: Overall, how do you rate our products on a scale from (1-5)?
Observe the above sequence of questions. It starts from the specific feature of a product to the overall performance of the product. If your survey takers give a high rating to the first 2 questions, they might be reluctant to give a lower rating to the product as a whole. A bias is being created in their mind with the first 2 questions that all the product features are good.
How to Avoid Question Order Bias
(a) While creating a customer satisfaction survey, start with questions that ask for an overall rating and then ask the feedback on specific product/service. This ensures that they do not create a positive or negative bias in their minds while answering questions that ask for the overall rating.
(b) Group together questions that belong to the same category. Make sure that you rotate the questions in the category to avoid inter-biases.
5. Answer Order Bias
Here, the survey takers have a tendency to select the first answer option in a multiple choice question or choose the last option in the answer list. The intent behind choosing the first answer option is because it is the first option read by the surveyees. They take it to be true.
On the other hand, choosing the last option is because of the recency effect, i.e, they tend to remember recent options more clearly and choose the same.
How to Avoid Answer Order Bias
(a) Use question randomization where the questions are shown randomly to the survey takers. With ProProfs Survey Maker, you can shuffle the answer options and display them in multiple ways.
(b) Minimize the options in the multiple choice questions but provide an option “Prefer not to say” to make the survey inclusive.
6. Extreme and Neutral Response Bias
These two types of responses are common in a Likert Scale type online questionnaire. Here, your survey respondents either select the most extreme options ‘least likely’ or ‘most likely’ or they stick to neutral options.
A person chooses extreme options either due to the strong emotional tone in the survey wording. While a neutral response is a result of disinterest in taking the survey. This could be due to lengthy survey or complex-unrelated questions.
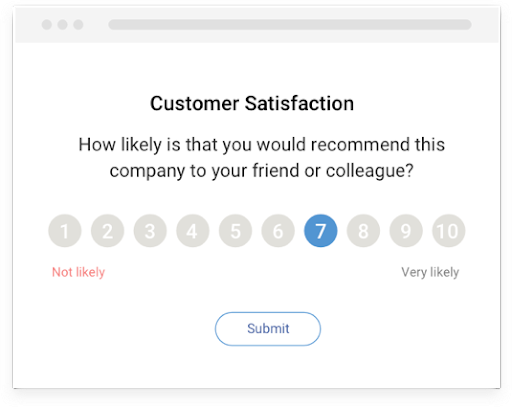
How to Reduce Extreme and Neutral Response Bias
(a) Avoid double barreled questions in a Likert scale question type. Double barreled questions are confusing and demand two opinions in a single question.
(b) Keep the survey question wording positive to reduce bias.
(c) Use simple and jargon free language to ensure easy understandability of the survey questions.
(d) Minimize the survey questions to keep the survey short and to the point.
7. Personal Bias

Image Source: Otomeyt
Your survey respondents personal beliefs, attitudes and experiences play a major role in their response to a survey. This can make them take a morally correct or incorrect stand. Sometimes, a morally correct approach may not be socially acceptable.
For example, if you ask your survey respondent, “Should death penalty be made legal?”, there could be a mixed answer due to one’s personal bias. Some of them will be of the opinion that death penalty is necessary to stop heinous crime while others might take a moral stand that death penalty is against ethics and morality.
How to Avoid Personal Bias in Your Survey
It is difficult to completely eliminate survey bias on a personal basis but you can reduce it with positive and neutral wording along with simple and jargon free language.
8. Non-Response Bias
A non-response bias arises when your survey respondents fail to answer certain survey questions or the entire survey altogether. This happens due to many reasons like lack of anonymity, long survey frequency and more.
For example, your employees may be reluctant to answer a non-anonymous employee engagement survey. They will be more open to talk about the workplace challenges if their anonymity is guaranteed. This could be due to fear of being reprimanded.
Also, in case of customer surveys, when you collect your customer’s feedback after a long interval of their product purchase, they may be unable to recollect the experience and give a reliable response. Most likely, they will choose to ignore your survey altogether.
How to Reduce Non-Response Bias
(a) Keep your survey short and simple to encourage more people to take up your survey.
(b) Make sure that you send your survey at every customer touchpoint like after a product purchase, after a customer support call, and more.
(c) Make use of different survey distribution channels like email, social media, website embedding, and more.
(d) Collect anonymous survey responses to ensure privacy of your survey respondents.
Reduce Survey Bias and Increase Your Survey Response Rates
Survey bias is an unavoidable part of any survey creation process. It can occur due to different reasons like personal beliefs of your survey respondents, survey sampling errors, survey question placement, survey answer options, and more.
You can easily eliminate survey bias with careful planning and testing of your survey. Ensure that you group similar survey questions and bring in random display of questions to avoid Q&A biases. Also, make use of positive and neutral wording of questions to make your survey less emotional and avoid extreme responses.
Looking to create a bias free survey? ProProfs Survey Maker comes with free survey templates types to create a versatile survey.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!

 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback!
 Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!